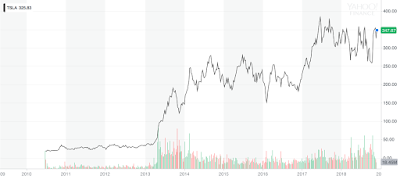
Source: Investopedia
An investment strategy that aims to capitalize on the continuance of existing trends in the market. The momentum investor believes that large increases in the price of a security will be followed by additional gains and vice versa for declining values.
An investment strategy that aims to capitalize on the continuance of existing trends in the market. The momentum investor believes that large increases in the price of a security will be followed by additional gains and vice versa for declining values.
More like moving with the market trends than value investing (based on fundamental analysis).